How to operate a drone safely and effectively is more than just mastering the controls; it’s about understanding the technology, respecting regulations, and appreciating the potential for breathtaking aerial photography and videography. This guide provides a step-by-step approach, from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers, ensuring you’re well-prepared for your drone adventures. We’ll cover everything from basic flight principles to advanced techniques, equipping you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
We’ll explore the intricacies of drone operation, delving into essential pre-flight procedures, navigating the complexities of drone controls and flight modes, mastering camera operation for stunning visuals, and maintaining your drone for optimal performance. We’ll also touch upon advanced techniques and safety protocols to ensure a safe and enjoyable flying experience. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to enhance your existing skills, this guide will serve as your comprehensive resource.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting the drone’s components, understanding local regulations, and preparing for potential emergencies. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents and damage.
Drone Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection is paramount to safe drone operation. This involves systematically checking each component for any damage or malfunction.
| Component | Inspection Item | Acceptable Condition | Unacceptable Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Visual inspection for cracks, chips, or bends | No visible damage; blades are firmly attached | Cracks, chips, or significant bends; loose blades |
| Battery | Check battery level and condition | Sufficient charge; no visible damage or swelling | Low charge; visible damage or swelling |
| Camera | Lens clarity and gimbal functionality | Lens is clean and free of obstructions; gimbal moves smoothly | Dirty or scratched lens; gimbal is stiff or unresponsive |
| Airframe | Check for any damage to the drone body | No cracks, dents, or loose parts | Cracks, dents, or missing parts |
Understanding Local Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Operating a drone requires adherence to local laws and regulations. Ignoring these rules can lead to hefty fines or legal repercussions. Understanding airspace restrictions is equally important to prevent collisions with other aircraft.
- No-fly zones: Airports, military bases, and other sensitive areas often have restricted airspace.
- Height restrictions: Many jurisdictions limit the maximum altitude for drone flights.
- Population density restrictions: Flying over crowded areas might be prohibited or require special permits.
- Privacy concerns: Flying over private property without permission is generally illegal.
Safe Flight Conditions Decision-Making Process

A clear decision-making process is vital to ensure safe drone operation. This flowchart guides the pilot through the critical steps involved in assessing flight conditions.
(Flowchart would be inserted here, depicting a decision tree based on weather conditions (wind speed, precipitation), airspace restrictions, battery level, and drone condition. The flowchart would lead to a “Safe to Fly” or “Unsafe to Fly” conclusion.)
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle emergencies is crucial for safe drone operation. Quick thinking and proper response can minimize damage and prevent accidents.
- Loss of signal: Most drones have a “return-to-home” (RTH) function that automatically brings the drone back to its starting point. If RTH fails, visually track the drone and attempt to regain signal.
- Low battery: Immediately initiate the RTH function and land the drone as soon as possible. Never let the battery completely deplete.
- Unexpected mechanical failure: Attempt controlled landing if possible. If not, prioritize safety and allow the drone to descend gently, if possible.
Understanding Drone Controls and Flight Modes: How To Operate A Drone
Mastering drone controls and understanding flight modes are essential for safe and efficient operation. This section covers the basics of controlling your drone and selecting the appropriate flight mode for your needs.
Drone Controller Functions
Standard drone controllers typically use two joysticks to control the drone’s movement. Each joystick controls specific aspects of the drone’s flight.
- Left Joystick (Yaw/Throttle): The left joystick controls the drone’s altitude (throttle) and its rotation (yaw). Pushing the joystick up increases altitude, pushing down decreases it. Rotating the joystick left or right rotates the drone.
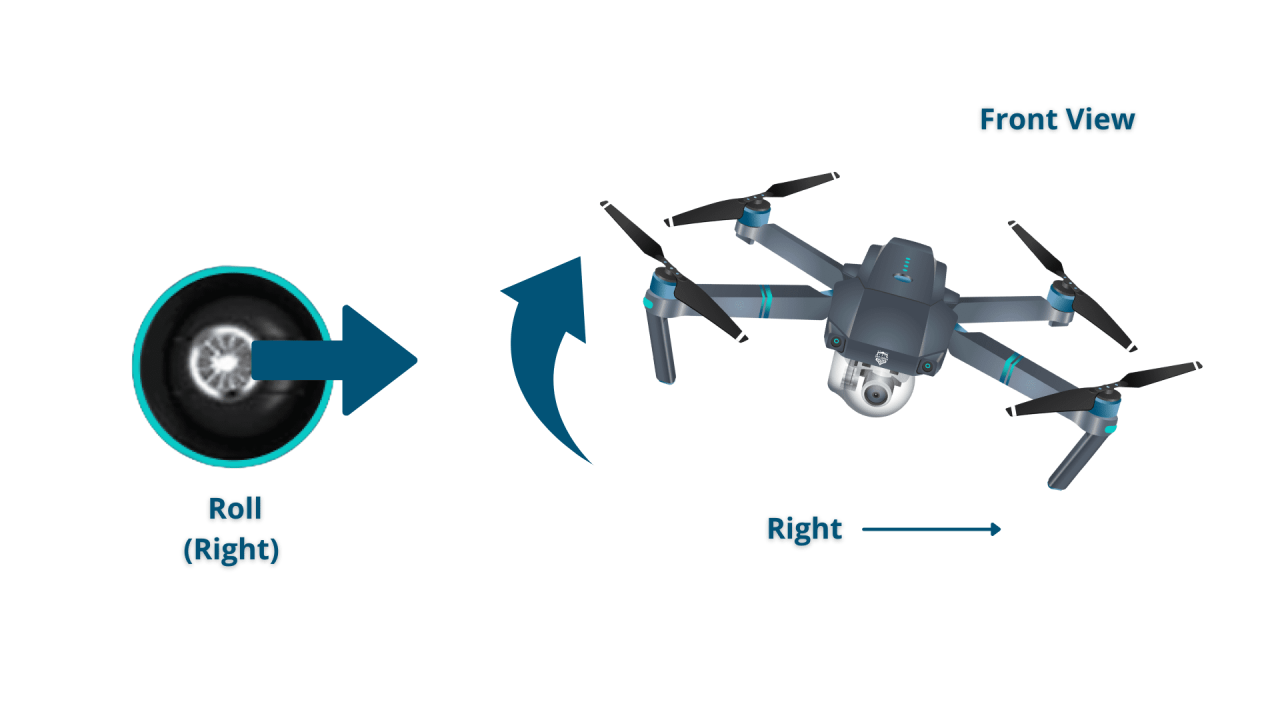
- Right Joystick (Pitch/Roll): The right joystick controls the drone’s pitch (forward/backward movement) and roll (left/right movement). Pushing the joystick forward moves the drone forward, pulling it back moves it backward. Pushing it left or right causes the drone to tilt and move laterally.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. Selecting the right mode is crucial for safe operation and maneuverability.
- Beginner Mode: Limits speed and responsiveness, ideal for learning.
- Sport Mode: Unlocks full speed and responsiveness, suitable for experienced pilots.
- GPS Mode: Utilizes GPS for precise positioning and stability, helpful for longer flights and complex maneuvers.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedures
Safe takeoff and landing are fundamental aspects of drone operation. Following these steps ensures a smooth and controlled flight.
Learning to operate a drone involves understanding its controls and safety features. A crucial first step is familiarizing yourself with the basics, which you can do by checking out this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. From there, practice in a safe, open area is essential before attempting more complex maneuvers. Mastering the art of drone operation takes time and dedication, but the results are well worth the effort.
- (Image description: Drone on the ground, propellers still. Caption: Pre-flight checks completed, ready for takeoff.)
- (Image description: Drone slowly lifting off the ground. Caption: Gentle and controlled ascent.)
- (Image description: Drone hovering at a low altitude. Caption: Maintaining stable hover before further maneuvers.)
- (Image description: Drone descending slowly towards the ground. Caption: Controlled descent for landing.)
- (Image description: Drone gently touching down on the ground. Caption: Safe and smooth landing completed.)
Basic Drone Maneuvers
Once comfortable with takeoff and landing, mastering basic maneuvers expands your drone’s capabilities.
- Hovering: Maintaining a steady position in the air.
- Ascending/Descending: Controlling the drone’s altitude.
- Moving Forward/Backward: Controlling the drone’s pitch.
- Turning: Controlling the drone’s yaw.
Camera Operation and Image Capture

The camera is a key feature of many drones, allowing for stunning aerial photography and videography. Understanding camera settings and techniques is essential for capturing high-quality images.
Camera Settings and Their Effects
Adjusting camera settings allows you to control various aspects of your images, impacting their overall quality and appearance.
| Setting | Description | Effect on Image |
|---|---|---|
| ISO | Sensitivity to light | Higher ISO increases sensitivity (useful in low light) but can introduce noise (grain). Lower ISO reduces noise but requires more light. |
| Shutter Speed | Duration the sensor is exposed to light | Faster shutter speed freezes motion, slower shutter speed creates motion blur. |
| Aperture | Size of the lens opening | Wider aperture (lower f-stop number) creates a shallower depth of field (blurred background), narrower aperture (higher f-stop number) creates a deeper depth of field (everything in focus). |
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
Achieving professional-looking aerial shots requires understanding different camera angles and perspectives.
- Experiment with different altitudes and angles to find the best composition.
- Utilize the drone’s gimbal for smooth and stable shots.
- Consider the lighting conditions and adjust settings accordingly.
- Practice panning and tilting the camera for dynamic shots.
Adjusting Camera Settings for Various Lighting Conditions
Different lighting conditions require different camera settings to achieve optimal image quality. Bright sunlight may require lower ISO and faster shutter speed, while low light might necessitate higher ISO and slower shutter speed.
Tips for Composing Visually Appealing Shots
Understanding basic composition techniques, such as the rule of thirds, leading lines, and symmetry, significantly enhances the visual appeal of your aerial shots. Avoiding common mistakes like overexposure, underexposure, and shaky footage further improves image quality.
Drone Maintenance and Battery Care
Regular maintenance and proper battery care are essential for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its safe operation. Neglecting these aspects can lead to premature wear and tear and potential malfunctions.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and enjoyable drone operation.
Drone Maintenance Schedule
Establishing a regular maintenance schedule helps prevent issues and ensures your drone remains in optimal condition.
- Weekly: Clean the drone body and propellers, inspect for any damage.
- Monthly: Tighten screws, check gimbal movement, and inspect battery connectors.
- Quarterly: More thorough inspection of all components, including motors and wiring.
Proper Battery Care
Proper battery care is critical for maximizing battery life and ensuring safe operation. Improper handling can lead to reduced performance and even fire hazards.
- Charging: Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger and follow instructions carefully.
- Storage: Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and heat sources.
- Handling: Avoid dropping or puncturing batteries.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Understanding common drone malfunctions and their causes aids in quick troubleshooting and prevents further damage.
- Propeller damage: Collisions or impacts can damage propellers, leading to unstable flight.
- Low battery performance: Overuse, improper storage, or aging batteries can reduce flight time.
- Gimbal malfunction: Physical damage or software issues can affect gimbal stability.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Addressing common problems promptly prevents escalation and ensures continued safe operation.
- Propeller damage: Replace damaged propellers with new ones.
- Low battery performance: Charge the battery fully, consider replacing older batteries.
- Gimbal malfunction: Check for physical obstructions, try recalibrating the gimbal, or contact support if necessary.
Advanced Drone Techniques and Features
Advanced features and techniques significantly enhance the capabilities of your drone, allowing for more complex and creative aerial operations.
Advanced Drone Features
Many modern drones offer advanced features that simplify complex maneuvers and enhance flight safety.
- Obstacle avoidance: Sensors detect and avoid obstacles, enhancing safety.
- Waypoint navigation: Pre-programmed flight paths allow for automated flights.
- Follow-me mode: The drone automatically follows a designated subject.
Planning and Executing Complex Flight Maneuvers, How to operate a drone
Planning and executing complex flight maneuvers requires careful consideration of factors such as wind conditions, battery life, and airspace restrictions. Thorough pre-flight planning is crucial for successful complex shots.
Improving Flight Stability and Precision
Practicing regularly and understanding the drone’s capabilities enhances flight stability and precision. Utilizing features like GPS and utilizing calm weather conditions significantly improves flight control.
Setting Up and Using Flight Planning Software
Flight planning software allows for detailed route planning and automated flight execution. This simplifies complex aerial photography and videography projects.
Operating a drone successfully combines technical skill with responsible awareness. By understanding pre-flight procedures, mastering the controls, and adhering to safety regulations, you can unlock the exciting possibilities of aerial exploration. This guide has equipped you with the foundational knowledge to confidently navigate the skies, capturing stunning visuals and experiencing the thrill of drone flight. Remember to continuously refine your skills, stay updated on regulations, and always prioritize safety.
Happy flying!
General Inquiries
What is the best drone for beginners?
Several user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, often featuring GPS stabilization and simplified controls. Research models with good reviews and consider your budget.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, flight conditions (wind, temperature), and usage (camera operation increases battery drain). Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
What happens if I lose signal with my drone?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that will automatically guide the drone back to its starting point if signal is lost. However, always fly within visual line of sight.
Can I fly my drone anywhere?
No. Drone regulations vary by location. Always check local and national airspace restrictions before flying. Unauthorized flights can lead to penalties.
